Key Takeaways
- Just as vinyl records offer a richer, more immersive listening experience, high-fidelity data provides deeper insights than summarized datasets.
- Many businesses underestimate the value of high-fidelity streaming data, yet it is essential for applications requiring precise analysis, like quantitative trading.
- In finance, tick-by-tick market data enables traders to conduct AS-IF analysis, refine predictive models, and identify profitable opportunities such as pairs trading.
- High-fidelity data benefits industries beyond finance, from diagnosing IoT-driven equipment failures in manufacturing to optimizing customer journeys in e-commerce.
- Time series databases are designed to store and analyze high-frequency, high-volume data streams, making high-fidelity data a strategic asset for innovation and competitive advantage.
Why does the gentle crackle of a vinyl record hold such a special place in our hearts? Analog experiences remain highly valued for their quality and tangible feel. The vinyl record renaissance exemplifies this – in the age of music streaming, many still appreciate vinyl’s richer, more immersive experience. Sometimes, a slower, higher-fidelity analog format offers an essential counterpoint to our instant-everything culture. It connects us to a level of quality and experience that digital struggles to replicate.
High data fidelity is crucial in data analytics too – especially for applications that deal with high-frequency time series data streams. Yet technologists often dismiss tuning into streaming data because they “don’t need to make real-time automated decisions.”
But they’re mistaken: rich, immersive, high-fidelity streaming data is for everyone.
Let’s explore the misunderstood importance in more detail, particularly in the context of market data and quantitative trading.
Understanding data fidelity
Data fidelity refers to the accuracy and completeness of data as it is captured and stored. Most companies “over-digest” data through down-sampling, complex transformations during ETL, summarization and aggregation, or statistical techniques. While these methods are sufficient to get a bird’s-eye view of activity—such as obtaining the close-of-day stock price—they fall short when rich, high-fidelity insight is required.
High-fidelity data management stores are in time-series order – meaning they are chronologically arranged within a sequence over time. This helps answer some of our most important questions about space, time, and order, and complements traditional, transactional data.
High-fidelity data by example in quantitative trading
Consider the world of financial market data and quantitative trading. Stock prices fluctuate hundreds of thousands, or even millions, of times a day. For many applications, a summarized version of this data is adequate — the price at each minute, hour, or end of the day.
However, high-fidelity data is indispensable for analysts and algorithmic traders who need to understand micro-movements and develop sophisticated trading strategies. For example, high-fidelity data allows for tick-by-tick analysis, where every price change is recorded and analyzed.
This level of detail is crucial for understanding the nuances of stock movements and conducting as-of analysis, a term used in time-series data analytics to compare time windows. As-of analysis makes it easy to compare today’s market conditions to the last similar situation so that traders can fine-tune today’s predictive model and trading strategies.
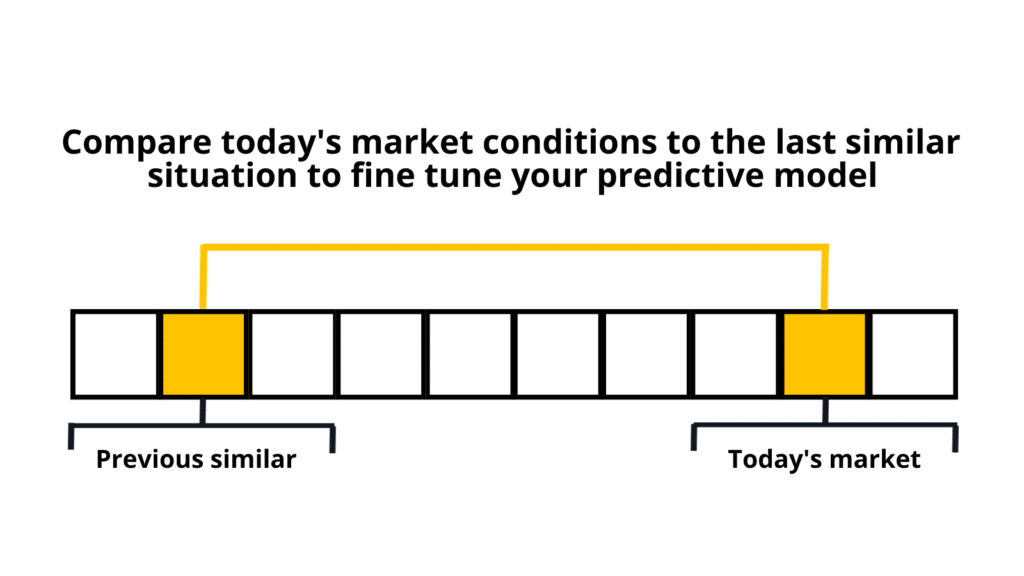
For example, high-fidelity data is essential to as-of comparison for ‘pairs trading’, where the price movements of related stocks are analyzed. Pairs trading capitalizes on the principle that the prices of related stocks tend to move together. However, trading opportunities arise when these stocks deviate from their usual patterns. Identifying these opportunities requires a detailed, tick-by-tick record of stock movements and other market indicators.
Comparing different windows in time helps traders anticipate how today’s market conditions might play out and predict the best trading strategies to employ by understanding data movements from previous, similar periods.
Applications beyond finance
The need for high-fidelity data extends beyond financial markets:
- For manufacturing applications involving the streaming of IoT (Internet of Things) sensor data, high-fidelity data can be crucial for diagnosing equipment failures. By replaying every sensor data change event, engineers can pinpoint the exact moment and cause of a failure
- In e-commerce, high-fidelity data can help understand customer behavior. By analyzing every click a user makes on their journey to checkout, businesses can identify where customers abandon their shopping carts, leading to more effective strategies for reducing cart abandonment rates
- In high-precision agricultural applications, drone and satellite imagery stream into the data analytics team. A high-fidelity view of data that overlays weather, soil quality, and irrigation, alongside imagery, can help industrialized agricultural teams analyze actions that optimize cost, safety, and yield.
In essence, any application with access to time-series streaming data has applications that benefit from a high-fidelity way of looking at their data.
The business advantage of high-fidelity data
Most companies struggle to store and analyze high-fidelity data due to the limitations of traditional relational and NoSQL databases, which are not optimized for time series data. This is where time series databases excel. They’re designed to handle high-frequency, high-volume data streams, making them ideal for storing and analyzing high-fidelity tick data.
The applications of high-fidelity data are numerous and varied, spanning industries from finance to manufacturing to e-commerce. Specialized time series databases handle and analyze this type of data, which sets it apart from other database management platforms.
As part of your innovation portfolio, exploring the possibilities of storing and analyzing high-fidelity tick or time series data can yield game-changing insight.
In summary, high-fidelity data is a technical requirement and a strategic asset that can drive significant business value. Read our ebook: 7 innovative trading applications and 7 best practices you can steal, to discover how to drive innovation and value with real-time and historical data in capital markets.