Risk Management Policy
Security Classification: Public
Version: 2.0 (February 2025)
The purpose of the KX Risk Management Policy is to establish requirements for managing, identifying, assessing, and controlling risk(s) facing KX. The policy also ensures that the information Security Management Systems (ISMS) can achieve its intended outcome(s), prevent undesired effects, and improve security practices within KX.
Scope
All KX information assets, applications and infrastructure are subject to the requirements of this policy. This policy must be adhered to by all temporary or permanent personnel and third parties who process, transmit or store any KX information or applications, or interact with or access any infrastructure or system.
- KX will implement a Risk Management Methodology which aligns to ISO 27005 and ISO 31000 frameworks. Risk Management provides a structured approach for identifying, analyzing, evaluating, prioritizing, and mitigating potential risks within our organization. The Risk Management Framework will be used to identify, assess, assign, manage and control new or existing risks
- Perform a compliance risk assessment against the ISMS annually or when a significant change occurs to determine areas of risk
- Implement risk management procedure(s) and include the following:
- Risk Assessment and assessment criteria
- Risk Treatment
- Risk Acceptance
- Risk Communication
- Risk Monitoring and Review
- Implement risk evaluation criteria which will consider the following:
- Strategic value of business information and assets
- Operational assets
- Criticality of information assets involved
- Legal and regulatory requirements, and contractual obligations
- Operational and business importance of availability, confidentiality, and integrity
- Stakeholders’ expectation and perceptions, and negative consequences for financial impacts and reputation
- Classify and prioritize all risks according to their score and importance to the organization
- The risk mitigation measures adopted by KX shall be effective in the long-term and to the extent possible be embedded in the business process of the organization.
- Risk Tolerance levels will be regularly reviewed and decided upon depending on the change in the company’s strategy.
The Risk Management Team shall perform a review of the Risk Management Policy annually or if a significant change occurs.
Risk Owners shall be responsible for overseeing and managing a specific risk or set of risks and is an accountable point of contact for risk at the senior leadership level. This includes determining mitigation, identification, and assessing risks.
Risk Management Components
Risk Assessment: Process of identifying events or functions that could negatively impact an organization’s ability to conduct business. These assessments help identify inherent business risks (impact on brand, reputation, legal requirements, operations, and finances) and provide measures, processes and controls to reduce the impact of these risks to business operations. Additionally, the Risk Assessment can identify opportunities, known as positive risks.
Risk Monitoring: Is an ongoing process and a crucial step in the risk management process. It is a continuous activity that results in the awareness of what is happening with risks across different parts of the organization.
Risk Owner: Any individual who is responsible for the management, monitoring and control of an identified risk, including the implementation of selected responses.
Risk Treatment Plan: A process of selecting and implementing measures to modify or treat risk. The treatment plan is developed based on the results of a Risk Assessment and is used to determine how to manage a risk down to an acceptable level.
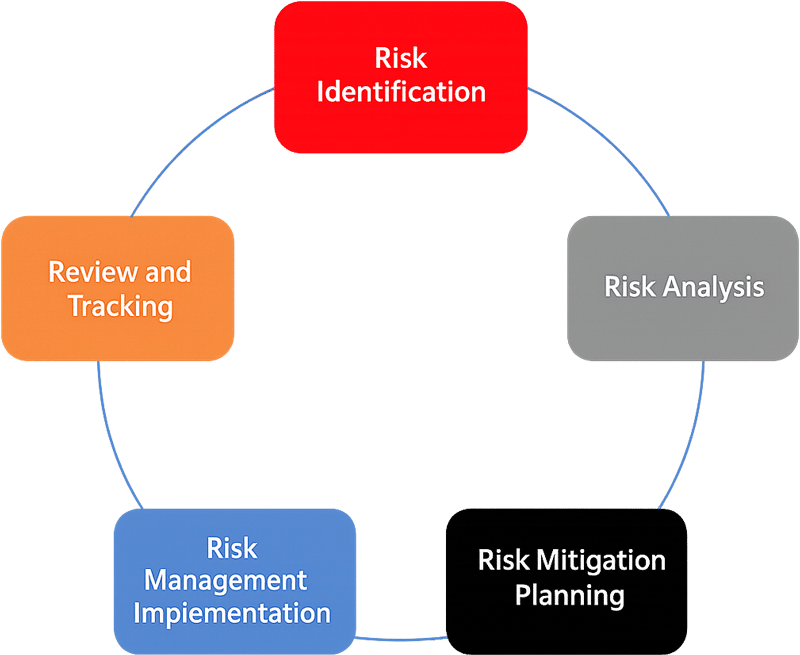
The below graphic represents the complete cycle of risk management. The Risk Methodology considers the context of KX and the requirements of the interested parties. The Risk Assessment process comprises of identifying, analysing and evaluating the risks by considering assets, threats and vulnerabilities. After the risks are analysed and evaluated, they are treated using the appropriate options considering the risk acceptance levels and criteria as defined by KX. Risk Management is a continuous monitoring process and includes communication with stakeholders at regular intervals.
Definitions:
- Asset: An asset may be anything belonging to, and of value to the company. For example, information assets (customer information), Software assets (applications), Hardware assets (servers), Location assets (data centers), and People (operations, management, KX staff).
- Control: Is a defined process or procedure to reduce risk.
- ISMS (Information Security Management System) – A collection of policies, procedures, and controls that ensure the confidentiality, integrity, and availability of KX data.
- Risk: a potential for loss or damage that could occur from a specific event or circumstance; A function of the likelihood of the event occurring and impacts it could have.
- Risk Management: The process of identifying, controlling, and minimizing uncertain events that could negatively impact system resources; – Risk assessment, mitigation strategies, continuous monitoring, and selecting, implementing, and assessing security controls.
- Compliance Risk is a potential risk for an organization to face legal penalties, financial loss, or other negative consequences if it does not adhere to regulations, laws, or KX internal policies.
- Operational Risk: Risks that can disrupt the flow of business operations or impact brand reputation and lead to direct or indirect financial losses such as technology failures, process inefficiencies or employee errors.
- Cybersecurity/Information Security Risk: The potential for loss of confidentiality, integrity, or availability of information or information systems; unauthorized access, use, disclosure, disruption, modification, or destruction of information and/or information systems.
- Threat: An occurrence of an undesired event which might compromise an aspect (confidentiality, integrity, availability) of an asset. Any circumstance or event (human or natural) with the potential to harm an information system through unauthorized access, destruction, disclosure, modification of data, and / or denial of service.
- Vulnerability: Weakness in an information system, system security procedure, internal controls, or implementation that could be exploited or triggered by a threat or threat source; glitch or weakness in software or hardware components that when exploited, results in a negative impact to confidentiality, integrity, or availability.